Open Academic Courses (AAM) – Greece
The Open Academic Courses (AAM) programme started at the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens (NKUA, the largest and oldest university in Greece and the entire Eastern Mediterranean, founded in 1837) as its main shareholder, developing more than 3,500 courses.
Background and context
The development of digital courses in Greece started in 2003, with the support of the Ministry of Education and the strategic contribution of GUnet, which made the Open eClass platform.
In 2010, an evaluation identified a need to upgrade the quality of digital courses and create a national search portal. The result was implementation of the programme Open Academic Courses (central development) and Central Register of Greek Open Courses (horizontal development), funded by the NSRF Programme 2007–2013 and 2014–2020.
Objectives and philosophy
The main objective of the programme was to open up academic courses to society, with an emphasis on quality, accessibility and intellectual property rights.
AAMs were designed as courses taught in Greek universities, freely accessible and freely available on the Internet for all (including under open Creative Commons licenses). The sub-objectives included:
- Strengthening the culture of open education in HEIs in the long term (information, awareness raising and staff training actions, etc.).
- Saving resources through shared infrastructure: common central AAM search portal, common AAM hosting platforms and multimedia video-type content (OpeneClass, Open Delos),equipment for centralised AAM and content hosting.
- Creating educational content that is accessible and useful to a wide audience, not only to students, but also to higher education graduates, students, professionals and in general to anyone who wishes to acquire new knowledge.
- Support creators (teaching staff) through technical teams and support staff.
Classification of courses and specifications
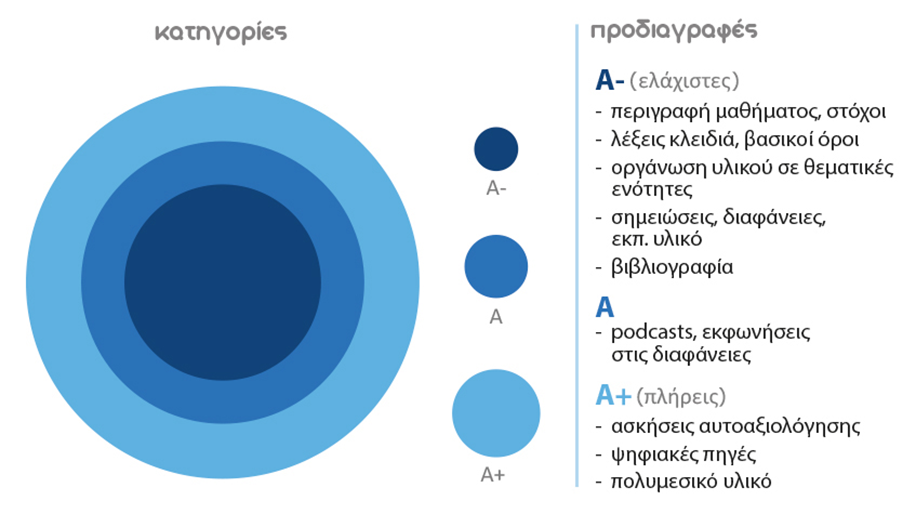
For quality assurance, AAMs were categorised into three categories:
- Category A-: Description, notes, bibliography, keywords
- Category A: All of the above plus synchronized audio (podcast format)
- Category A+: All the above and additional video lectures, self-assessment exercises, multimedia tools
These categories enable the gradual integration of teachers (and users) into the logic of open teaching, enhancing participation without presupposing a high technological level from the outset.
Why is this a good practice?
- Over 3 500 high-quality AAMs from 25 Greek universities
- More than 1,100 Type A+ courses and more than 80 Type A courses (with sound)
- AAMs account for 7.7% of all courses delivered in Greek universities (45,000)
- More than 3,600 faculty members participated with their own courses
- More than 500 technical and scientific staff supported the development of AAMs
- Over 20,000 educational videos
- Three (3) National Infrastructures: Open eClass, Open Delos, National Portal opencourses.gr
- More than 400,000 unique visits per month to institutional AAM platforms
- 4 Open Courses with concise and detailed instructions exclusively for teaching staff and AAM development support staff, such as intellectual property rights, development of educational material for people with disabilities and AAM development issues
- The programme was awarded the 2016 Open Education Award for Excellence, in the Creative and Innovative Projects category
The contribution of the above initiative to the promotion and provision of science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM)-related courses is of the utmost importance, exceeding a total of 1,500, i.e. more than half of all AAMs.
Benefits for teachers and HEIs
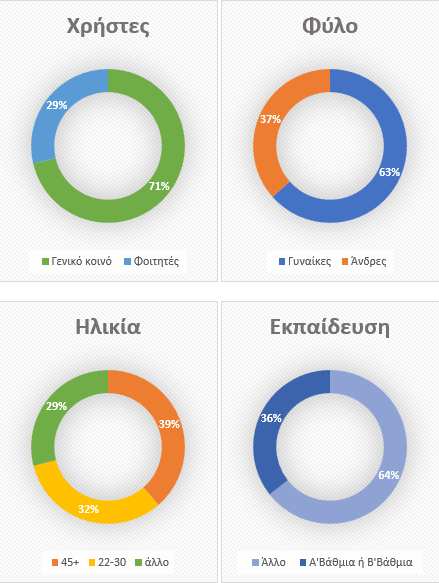
The technological and pedagogical support offered to teachers through the support structures was recognized. Of the 57 AAM teachers/creators who replied to the questionnaire:
- 100% gave a positive assessment of the quality and integrity of digital and multimedia material
- 96.5% said they were satisfied with the experience of AAM development
- 98.25% would recommend joining colleagues
- 94.7% believe that AAMs help with attendance
AAMs have had multiple positive effects on Greek HEIs, including:
- Extroversion: opening of HEIs to society and international presence
- Social policy: supporting students with disabilities, financial or geographical barriers
- Teaching practice: enhancing teachers' digital skills, strengthening the concept of Open Education in the Greek academic community
- Infrastructure: developing new hosting services and systems
- Policies: formation of public policies of open education in Greek public state institutions
Challenges included the needs for constant information and training of teaching staff, design for accessibility, rights and multimedia the ability to certify knowledge in a large-scale and sustainable way, balancing development costs with quality on offer. The experience of HEIs has shown that success depends on providing support to creators and having a strategy, not just funding.
Looking to the future
The long-term implementation of the programme has shown the maturity of the Greek academic system in terms of the production of open educational content, the social impact of the project, and the need for continuity – both with a new cycle of projects and with the institutional consolidation of open education.
Proposals for the future include:
- Institutionalisation of open education
- Re-engage digital platforms with information campaigns
- Development of courses with the possibility of certification
- Creation of collaborative communities of practice among HEIs
The AAM Programme is not only an infrastructure and content project, but a digital heritage for higher education and society at large.